Comparing Business Models to Sales Models
For startups entrepreneurs, there’s is often a blending together of business models and sales models. Here’s a way to think about it, for both tech and non tech companies.
Business Models
Business models include the purpose, strategy, competitive advantage, ecosystem (Partner and Channel) and of course the product or services. Too often we take these items for granted and think of it simply as a tech business model or software business model. This can be a euphemism for “I have a cool product and don’t know if anyone will buy it”.
This isn’t horrific as long as you have a proxy model in mind for your company. For example, my startup is like Salesforce.com (subscription model, sold to business) or like AirBNB (transactional fee paid for the marketplace of connecting buyers and sellers of rooms).
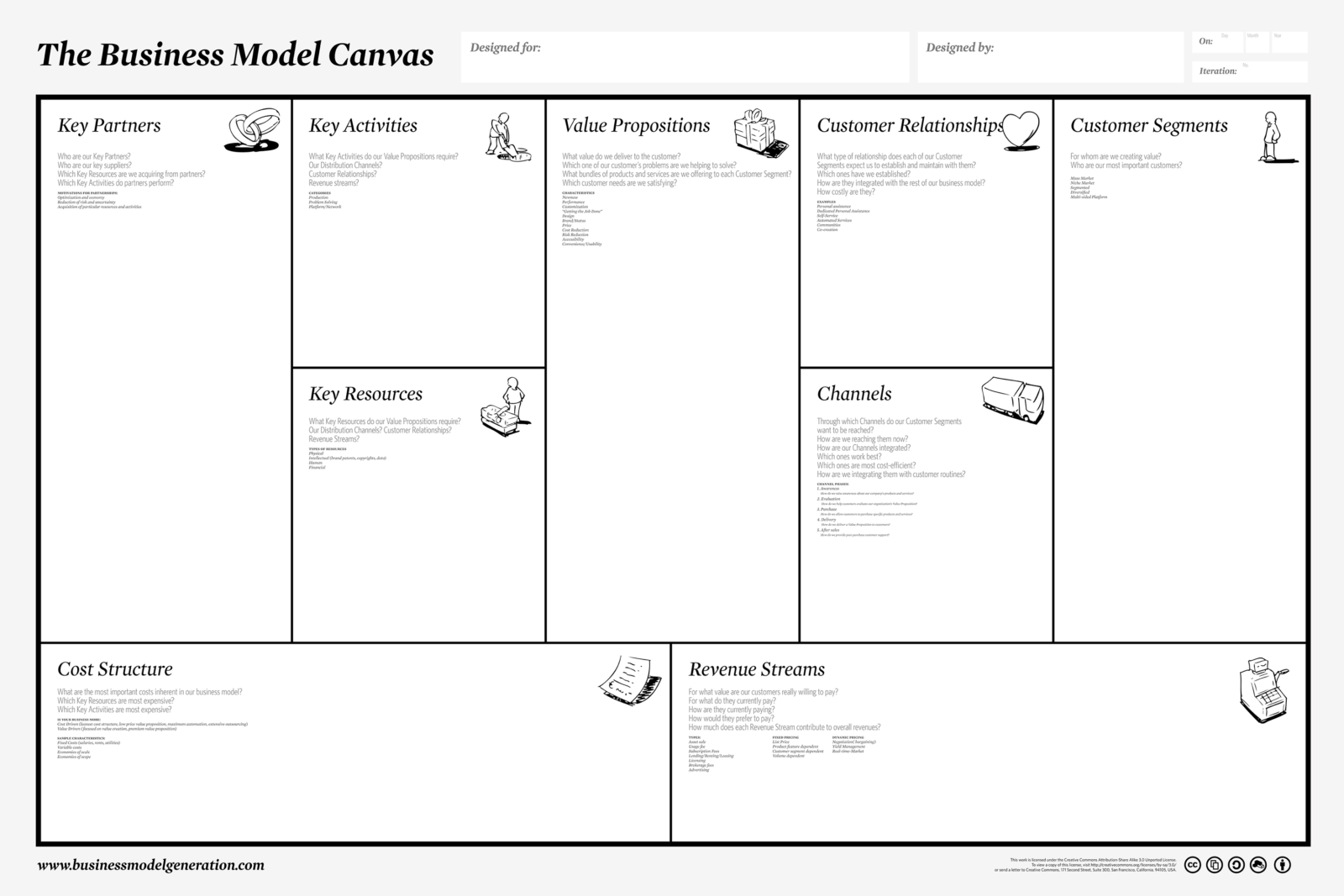
If you don’t have a proxy, I’d suggest you start with the following exercise. There is a great book called Business Model Generation – available in both a book version or via a iPad App called Business Model Toolbox.
Alexander Osterwalder and the team of authors have outlined a great method and process to outline your business model. I’ve included the canvas below, or you can download the PDF here. I’d suggest taking a few minutes and fill out the boxes and galvanize some of your thoughts on your business model.
- Value proposition
- Infrastructure
- Customers
- Finances
- Etc.
Now that you have a start on your business model, let’s talk about how you are going to sell the cool product.
Sales Models
Is how you take your product or service to market. Let’s start with question one: Are you selling to a Business (B2B) or to a Consumer (B2C). You have to pick which market you will serve, if you have a question start with who will be paying for your product? If the consumer benefits, but you charge a retailers for an app, you’re a B2B company.
Remember, nothing happens (for revenue) until something gets sold. That point of SALE is your sales model. Here are you options:
- Web Sales– the customer finds you via the internet search or outbound marketing, comes to your website and transacts their sale over the web.
- Inbound marketing – is a buzz with companies like HubSpot and SEO. Inbound marketing requires that someone is looking for you and that you use these tools to be found on the web.
- PROBLEM – The challenge of “Innovation” is that no one is looking for your new wiz bang idea because they don’t know it exists. so you won’t be able to optimize around search terms.
- Outbound Marketing – uses digital and traditional marketing to drive traffic back to your website to transact.
- What doesn’t work in Web Sales? Relationship sales don’t work – consulting, big-ticket items (though you can generate leads for Direct Sales)
- What does work? Amazon with books is a great example of a category, a book is a book, or a TV a TV. What you get online is the same product or service. Software subscriptions work, if the risk of purchase is low. Salesforce.com still positions their product as a monthly fee, but you’ll have to pay annually. Your startup won’t have that luxury.
- Inbound marketing – is a buzz with companies like HubSpot and SEO. Inbound marketing requires that someone is looking for you and that you use these tools to be found on the web.
- Direct Sales–
- Inside Sales – this can be either inbound sales – someone calling into Staples to order a toner cartridge, or outbound sales, where call center agents call a warm or cold call list of prospects. I cut my teeth in sales doing this for a large stock broker – if you haven’t seen Boiler Room go watch it now
- Outside Sales – is a face to face sales effort. Typically you think of the car sales person or the copier sales person. But this area includes the very high-end of the sales effort that requires a huge amount of expertise – medical equipment, airplanes, enterprise software.
- PROBLEM – unless you are truly selling an enterprise solution, you are not going to be able to scale a sales force to do outside sales without a significant price point.
- What doesn’t work in Direct Sales – small ticket price doesn’t work because you have to pay to build (and scale) a sales team. You may be able to hire a rep or two, but if the price point is under $1,000-2,000 you won’t be able to build a scalable sales organization
- What does work? Large price point, relationship sales, enterprise sales cycle or complex sales cycles (multiple buyers and influencers)
- Channel Sales– or Indirect Sales – is where agents or resellers sell the product for you and either you or the reseller delivers the product. Think Microsoft product sales where you can’t buy directly from MS, but through a reseller partner
- Channels fulfill the demand for products – they don’t create demand for product. What do I mean? In the Microsoft example, for every $1 in software the channel expects $3-6 in services required to install, configure and support the product. The channel is in the customer to sell the services, not to sell 10% or less mark up on the software.
- Affiliates marketing – Affiliate marketplaces, like Clickbank is a great alternative to building a channel, if your product is a virtual good or is easily sold via the Affiliate model.
- What doesn’t work in Channel Sales? If you product requires you to evangelize the marketplace, you won’t sell it through a channel. Or if you product competes for the same budget $$ as your partner, they will sell their product and not push yours.
- What does work? When your product is an incremental sale for your channel and can produce incremental profit – think of the extended warranty for your new car. You have to make sure you offer is SUPER simple however.
- Retail Sales– the traditional Department or retail store route of delivering a physical good to a customer.
- If you have a physical product that needs shelf space at Best Buy or Target
- If you need logistics for your product to get to the customer
- Be ready to pay for placement in shelf space
- What doesn’t work in Retail – virtual goods don’t work well in retail – they tend to be too abstract. Complex product that require time to explain.
- What does work in Retail – complimentary products to the existing customer base.
There are a lot of options for variation within these four models. But I can’t think of another point of Sale, can you? Add a comment on the Blog.